Table of Contents
ISO 9001 Certification Cost
While the cost of implementation varies to the extreme (e.g., cost of consultants, training of personnel, opportunities lost due to delayed/slow implementation), the cost of ISO 9001 certification can be reasonably approximated.
Companies must be aware that their certification contract lasts 3 years. After the first 3-year period, the company may continue its certification under a new contract with the CB (Certification Body – aka Registrar) that they’ve selected… where the cost typically goes down slightly.
The first 3-year Cycle
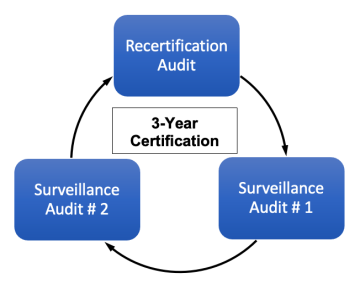 The first 3-year cycle includes an “Initial” Audit” which consists of Stage 1 & Stage 2 audit activities. After successful completion of the Stage 2 audit, along with verification and closure of any nonconformities identified, the company will receive its certification. This is followed by 2 (two) “Surveillance” audits. At that point, the company has the opportunity to renew its certification for another 3-year term.
The first 3-year cycle includes an “Initial” Audit” which consists of Stage 1 & Stage 2 audit activities. After successful completion of the Stage 2 audit, along with verification and closure of any nonconformities identified, the company will receive its certification. This is followed by 2 (two) “Surveillance” audits. At that point, the company has the opportunity to renew its certification for another 3-year term.
The continuing certification audits begin with a “Reassessment” audit that covers the entire scope of the certification. This is then followed by another two (2) “Surveillance” audits. And the process repeats.
This means, unless the company is growing in size, that the first 3-year cycle will be the most expensive. I will cover the specifics of “how” that cost is calculated below. So open a blank spreadsheet (or get your pen & calculator ready) and I’ll show you how to calculate your approximate costs relating strictly to ISO 9001 certification EXCLUDING the travel & living expenses of the auditor(s)… which can be a significant, separate cost if the CB you select doesn’t have auditors in your immediate area.
Estimating the Cost of ISO 9001 Certification
The following is a step-by-step guide for estimating ISO 9001 certification cost.
1. Every CB charges a fixed fee covering the “Certification Management” (aka, “Certificate Administration”, “Maintenance Fee”). This fee is separate from the audit day rates because these fees are fixed for each individual certificate or site. Some of the activities that this fee covers include:
- Customer Service Representatives (CSRs) or Schedulers time
- Management of the actual certification (tracking the upcoming and past audits)
- Technical Reviews of each completed audit report (to ensure compliance with ISO 17021-1)
- Tracking and closing nonconformities
While this fee varies from one CB to the next, these average approx. $500 per certificate/site (±$100). For AS91xx certificates, there is an additional standard $500 annual fee (for OASIS).
2. Every CB (Certification Body – aka Registrar) has an “Audit Day Rate”. During 2023 I polled 10 CBs and found that this rate averaged $1,500/day (±$300) for ISO 9001 (add $100/day for AS91xx certification).
3. All CBs are required to consult IAF MD 5, “Determination of Audit Time of Quality, Environmental, and Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems” (available free) to determine the number of audit days required for each audit (the “MD” designator means that it is a “Mandatory Document”). This determination begins by obtaining the number of personnel at the company who will be involved with the company’s Quality Management System (QMS).
IAF MD 5 defines applicable personnel as:
1.9. Effective Number of Personnel
The effective number of personnel consists of all personnel (permanent, temporary, and part-time) involved within the scope of certification including those working on each shift. When included within the scope of certification, it shall also include non-permanent (e.g. contractors) personnel.
Personnel not involved with the QMS typically include those individuals who have absolutely no direct or indirect involvement with customers or fulfilling customer requirements. Examples may include cafeteria personnel, groundskeepers, janitorial, and/or security personnel within a manufacturing company. Also, there are no direct requirements in ISO 9001 for Accounting/Financial functions… even though Accounts Receivable invoices to customers.
4. The CB then consults IAF MD 5, “Table QMS 1 – Quality Management Systems” (found in “Annex A – Quality Management Systems”)… shown below, to match the number of personnel at the company to the range found in the “Effective Number of Personnel” column. This will indicate the “Audit Time Stage 1 + Stage 2 (days)”.
| Relationship between Effective Number of Personnel and Audit Time (Initial Audit only) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Number of Personnel | Audit Time Stage 1 + Stage 2 (days) | Effective Number of Personnel | Audit Time Stage 1 + Stage 2 (days) |
| 1-5 | 1.5 | 626-875 | 12 |
| 6-10 | 2 | 876-1175 | 13 |
| 11-15 | 2.5 | 1176-1550 | 14 |
| 16-25 | 3 | 1551-2025 | 15 |
| 26-45 | 4 | 2026-2675 | 16 |
| 36-65 | 5 | 2676-3450 | 17 |
| 66-85 | 6 | 3451-4350 | 18 |
| 86-125 | 7 | 4351-5450 | 19 |
| 126-175 | 8 | 5451-6800 | 20 |
| 176-275 | 9 | 6801-8500 | 21 |
| 276-425 | 10 | 8501-10700 | 22 |
| 426-625 | 11 | >10700 | Follow progression above |
5. The CB will then make adjustments to the number of audits days determined from “Table QMS 1” based upon the complexity of the company (Ref. IAF MD 5, Figure QMS 1 – Relationship between Complexity and Audit Time) and associated risks of its products and/or services (Ref. IAF MD 5, Annex A, Table QMS 2 – Examples of Risk Categories).
IAF MD 5
Table QMS 2 – Examples of Risk Categories
These risk categories are not definitive, they are examples only that could be used by a CB when determining the risk category of an audit.
High Risk
Where failure of the product or service causes economic catastrophe, or puts life at risk. Examples include but are not limited to:
Food; pharmaceuticals; aircraft; shipbuilding; load-bearing components and structures; complex construction activity; electrical and gas equipment; medical and health services; fishing; nuclear fuel; chemicals, chemical products and fibres.
Medium Risk
Where failure of the product or service could cause injury or illness. Examples include but are not limited to:
Non load bearing components and structures; simple construction activities; basic metals and fabricated products; non-metallic products; furniture; optical equipment; leisure and personal services.
Low Risk
Where failure of the product or service is unlikely to cause injury or illness. Examples include but are not limited to:
Textiles and clothing; pulp, paper and paper products; publishing; office services; education; retailing, hotels and restaurants.
In order to understand how audit days and be reduced (or increased) it is important to understand the difference between the terms “Audit Time” and “Audit Duration”.
For a simple (low complexity) company providing products/services in a low-risk category, the CB is allowed to reduce the audit time by up to 30% (Ref. IAF MD 5, sec. 3.9). However, if the company is complex and/or providing products/services in a high-risk category, then the CB can add time to the audit (IAF MD 5 provides no guidance on how much time may be added). Later, additional audit time may also be determined necessary due to new “risks”, such as “the results of any prior audits” (Ref. ISO 17021-1, sec. 9.1.4.2)
IAF MD 5, sec. 2.1.2 states “the duration of a management system certification audit should typically not be less than 80% of the audit time…”. The CBs read this “should” as “shall”.
6. After making adjustments to the audit time based on complexity and risk, the CB will determine the number of days required for the “Stage 1” audit (sometimes called a “Document Review”). While the “Stage 1” audit is typically a one-day audit, it could be 2 days (or more) for very large or complex businesses. The “Stage 1” audit is intended to ensure that the company is prepared for a full audit of their QMS (Ref. ISO 17021-1:2015, sec. 9.3.1.2). The Stage 1 audit will verify that the company has:
- Documented an appropriate “Scope” (Ref. ISO 9001 Auditing Practices Group Guidance on: Scope and applicability)
- Established and is monitoring quality-related “Key Performance Indicators” (KPIs) & Objectives
- Defined the processes and their interaction
- Identified any applicable quality-related Statutory and Regulatory requirements
- Completed an Internal Audit covering their entire QMS
- Performed a Management Review
The remainder of the audit days are allocated to the “Stage 2” audit… which will assess the entire scope of the certification.
7. After completing the “Initial” Audit” (Stage 1 & Stage 2 audit), the next two (2) audits will be Surveillance audits with each covering approx. half of the applicable requirements of ISO 9001, The time allocated for a Surveillance audit will be 1/3 of the days determined from IAF MD 5, “Table QMS 1 – Quality Management Systems” (Ref. IAF MD 5, sec. 5 “Surveillance”) after adjustments for complexity and risk… rounded up to the nearest half day.
8. After successfully completing two (2) Surveillance audits, the initial 3-year contract ends… and the company will be offered the opportunity to renew its certification contract. This time, there will be no “Stage 1” audit. And the recertification audit will be 2/3 of the audit days determined by the CB (Ref. IAF MD 5, sec. 6 “Recertification”) after adjustments for complexity and risk… rounded up to the nearest half day.
Multi-Site Businesses
If your company is a multi-site, there are additional criteria that must be taken into account. With the information above, reference, IAF MD 1, "IAF Mandatory Document for the Audit and Certification of a Management System Operated by a Multi-Site Organization", which identifies a multi-site organization as:
IAF MD 1, sec. 2.4 Multi-site Organization
An organization covered by a single management system comprising an identified central function (not necessarily the headquarters of the organization) at which certain processes/activities are planned and controlled, and a number of sites (permanent, temporary or virtual) at which such processes/activities are fully or partially carried out.
 If you’re ready for a path forward now…
If you’re ready for a path forward now…
Just click here to schedule your FREE Certification Strategy Meeting (via Zoom) with me. I’ll answer any questions you might have. No sales pitch. Just information.
Or, for my cell phone & e-mail address, visit the contact us page.
100% of our clients achieve certification on their first attempt.
This means that no CB has ever required a “follow-up” or “special” audit for any of our clients prior to being issued their certification.
We provide you with “peace of mind” that we'll take care of QMS certification!

